A comet-shaped region surrounding the earth and other magnetic planets in which the charged particles of the solar wind are controlled by the planet’s magnetic field rather than the sun’s magnetic field. It extends for some 60 000 km on the side facing the sun but on the opposite side it extends to a much greater extent. The boundary of the magnetosphere is known as the magnetopause. The magnetosphere of the earth includes the Van Allen belts. The detailed arrangements of magnetospheres are different in each magnetic planet.
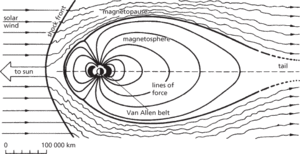
Magnetosphere and magnetopause.
The volume of space surrounding a planet, within which its magnetic field dominates external fields. Significant magnetospheres exist around Mercury, Earth, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune. The solar wind compresses a planet’s magnetosphere in the sunward direction and draws it out downwind into a long magnetotail. Planetary magnetospheres can be regarded as teardrop-shaped cavities in the solar wind.
The volume of space, surrounding a planet, in which the planet's magnetic field has a significant influence. The Earth's magnetosphere extends 64 000 km towards the Sun, but many times this distance on the side away from the Sun. That of Jupiter is much larger, and, if it were visible, would appear from the Earth to have roughly the same extent as the full Moon. The Russian-led space missions Coronas-I (launched in 1994) and Coronas-F (launched in 2001) were designed to investigate the magnetosphere of the Sun.
The Earth's magnetosphere is not symmetrical. The extension away from the Sun is called the magnetotail. The outer edge of the magnetosphere is the magnetopause. Beyond this is a turbulent region, the magnetosheath, where the solar wind is deflected around the magnetosphere. Inside the magnetosphere, atomic particles follow the Earth's lines of magnetic force. The magnetosphere contains the Van Allen radiation belts.
The space around a planet in which ionized particles are affected by the planet’s magnetic field. The Earth’s magnetosphere reaches far beyond the atmosphere. In the magnetosphere, charged particles are concentrated at altitudes of about 3000 km and 16 000 km. The charged particles oscillate between the northern and southern hemispheres. The outer boundary of the magnetosphere is sharp and well defined, extending to about 10 Earth radii on the sunlit side of the Earth and to perhaps 40 Earth radii on the dark side; but the boundary changes its position in response to solar activity, being depressed by the solar wind. See also exosphere; ionosphere.
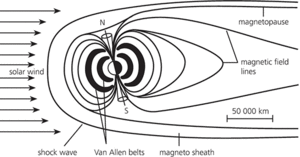
Magnetosphere
- Irgun
- iridescence
- iridescent clouds
- Iridium
- iridium
- iridium anomaly
- Iridium NEXT
- Irigaray, Luce (1930–)
- Irigoyen, Hipólito (1850–1933)
- IRIS
- Iris
- iris
- iris biometrics
- Irish elk
- Irish Famine (1845–51)
- Irish Free State
- Irish Republican Army
- Irish Republican Brotherhood
- IRLS
- IRM
- iron
- Iron Age
- iron age
- Iron Curtain
- iron formation