A device for measuring atmospheric pressure. The mercury barometer in its simplest form consists of a glass tube about 80 cm long sealed at one end and filled with mercury. The tube is then inverted and the open end is submerged in a reservoir of mercury; the mercury column is held up by the pressure of the atmosphere acting on the surface of mercury in the reservoir. This type of device was invented by the Italian scientist Evangelista Torricelli (1608–47), who first noticed the variation in height from day to day, and constructed a barometer in 1644.
In such a device, the force exerted by the atmosphere balanced the weight of the mercury column. If the height of the column is h and the cross-sectional area of the tube is A, then the volume of the mercury in the column is hA and its weight is hAρ, where ρ is the density of mercury. The force is thus hAρg, where g is the acceleration of free fall and the pressure exerted is this force divided by the area of the tube; i.e. hρg. Note that the height of the mercury is independent of the diameter of the tube. At standard atmospheric pressure the column is 760 mm high. The pressure is then expressed as 760 mmHg (101 325 pascals).
Mercury barometers of this type, with a reservoir of mercury, are known as cistern barometers. A common type is the Fortin barometer, in which the mercury is held in a leather bag so that the level in the reservoir can be adjusted. The height is read from a scale along the side of the tube in conjunction with a vernier scale that can be moved up and down. Corrections are made for temperature.
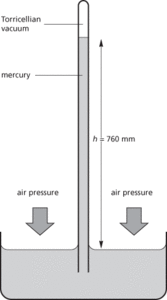
Mercury barometer.
The second main type of barometer is the aneroid barometer, in which the cumbersome mercury column is replaced by a metal box with a thin corrugated lid. The air is removed from the box and the lid is supported by a spring. Variations in atmospheric pressure cause the lid to move against the spring. This movement is magnified by a system of delicate levers and made to move a needle around a scale. The aneroid barometer is less accurate than the mercury type but much more robust and convenient, hence its use in altimeters.
An instrument used to measure atmospheric pressure. Early barometers consist of a tall vertical glass column containing mercury. The top of the column is sealed, while the bottom is open in a reservoir of mercury. The pressure of air on the reservoir balances the vertical column of mercury, from which the pressure can be read directly. Standard atmospheric pressure (101.325 kPa) corresponds to a height of 760 mmHg. The space above the mercury in the top of the leg is called a Torricellian vacuum. It is not a true vacuum but is the vapour pressure of the mercury.
Instrument for the measurement of atmospheric pressure. The usual type is a mercury barometer, in which the atmosphere’s pressure on a small reservoir of mercury supports a column of mercury in a vacuum tube the open end of which is below the surface of the mercury in the reservoir. The column is on average about 76 cm (30 inches) high. Readings must be corrected to compensate for pressure variation due to gravitational anomalies and for thermal expansion or contraction of the mercury; therefore correction to a standard temperature is necessary. See also aneroid barometer; fortin barometer; kew barometer.
- additive model
- additive primary colours
- additive process
- additive synthesis
- Addled Parliament (5 April–7 June 1614)
- add-on
- add-on manager
- add-on virus
- address
- addressability((of a display device))
- addressable location
- address book
- address bus
- address calculation sorting
- address format
- address harvester
- addressing
- addressing mode
- addressing schemes
- address mapping
- address mark
- address munging
- address register
- address-relative
- address resolution