Two compound statements involving the same components are logically equivalent if they have the same truth tables. For example, the truth table for the statement (¬p) ∨ q is:
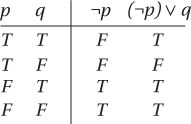
By comparing the last column here with the truth table for p ⇒ q (see implication), it can be seen that (¬p) ∨ q and p ⇒ q are logically equivalent. This equivalence is the basis of proof by contradiction.
- Airy, George Biddell (1801–92)
- Airy model
- Airy phase
- Airy, Sir George Biddell
- air–sea interaction
- AISat
- aitia
- Aitken Double Star Catalogue
- Aitken estimator
- Aitken nuclei
- Aitken nuclei counter
- Aitken nucleus
- Aitken, Robert Grant
- Aitken, Robert Grant (1864–1951)
- Aitken’s method(in numerical analysis)
- Aitken’s Δ2 process
- AIUI
- AIV
- AI Velorum star
- AIW
- AIX
- Aix‐la‐Chapelle, Treaty of (1748)
- AJ
- Ajax
- Ajdukiewicz, Kazimierz (1890–1963)