1. A scale of measurement in which an increase or decrease of one unit represents a tenfold increase or decrease in the quantity measured. Decibels and pH measurements are common examples of logarithmic scales of measurement.
2. A scale on the axis of a graph in which an increase of one unit represents a tenfold increase in the variable quantity. If a curve y=xn is plotted on graph paper with logarithmic scales on both axes, the result is a straight line of slope n, i.e. logy=nlogx, which enables n to be determined.
A method of representing positive numbers on a line as follows. Taking one direction along the line as positive, and a point O as origin, the number x is represented by the point P in such a way that OP is proportional to log x, where logarithms are to base 10. Thus the number 1 is represented by O; and, if the point A represents 10, the point B that represents 100 is such that OB = 2OA.
The measurement of sound using decibels and of the size of earthquakes using the Richter scale are two examples of logarithmic scales.
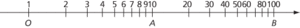
A logarithmic scale
See also slide rule.
1. A scale of measurement in which an increase or decrease of one unit represents a tenfold increase or decrease in the quantity measured. Decibels and pH measurements are common examples of logarithmic scales of measurement.
2. A scale on the axis of a graph in which an increase of one unit represents a tenfold increase in the variable quantity. If a curve y = xn is plotted on graph paper with logarithmic scales on both axes, the result is a straight line of slope n, i.e. logy = nlogx, which enables n to be determined.
A scale of measurement in which an increase or decrease of one unit represents a tenfold increase or decrease of that measurement: pH measurement is an example of a logarithmic scale. Data that follows a logarithmic relationship can be plotted on special graph paper with a logarithmic scale. Alternatively, the relationship can be linearized. For example, the Fanning friction factor for turbulent flow in smooth pipes is related to Reynolds number as . This can be represented as a linear relationship on a plot of ln f versus ln Re. This is a straight line, therefore which enables the gradient b to be determined.
A scale of measurement in which an increase or decrease of one unit represents a tenfold increase or decrease in the quantity measured. Decibels and pH measurements are common examples of logarithmic scales of measurement.
A scale on a diagram where distances from the origin represent the logarithm of a variable. Logarithmic scales are used particularly in diagrams with time on one, usually the horizontal, axis, and some real or nominal variable such as gross domestic product or the price level on the vertical axis. The slope of a curve in such a diagram shows the proportional growth rate of the variable, and a constant proportional growth trend is represented by a straight line. If both axes use logarithmic scales, the slope of a curve is proportional to the elasticity of one variable with respect to the other. Neither zero nor negative numbers can be represented on a Logarithmic scale.
- Actium, Battle of
- activated adsorption
- activated alumina
- activated carbon
- activated charcoal
- activated complex
- activated-complex theory
- activated sludge process
- activation analysis
- activation energy
- activator
- active
- active antenna
- active area
- active attack
- Active Cavity Radiometer Irradiance Monitor Satellite
- active code
- active component
- active constraint
- active current
- active device
- Active Directory
- active euthanasia
- active filter
- active galactic nucleus