A nucleotide that is of fundamental importance as a carrier of chemical energy in all living organisms. It consists of adenine linked to d-ribose (i.e. adenosine); the d-ribose component bears three phosphate groups, linearly linked together by covalent bonds (see formula). These bonds can undergo hydrolysis to yield either a molecule of ADP (adenosine diphosphate) and inorganic phosphate or a molecule of AMP (adenosine monophosphate) and pyrophosphate. Both these reactions yield a large amount of energy (about 30.6 kJ mol-1) that is used to bring about such biological processes as muscle contraction, the active transport of ions and molecules across cell membranes, and the synthesis of biomolecules. The reactions bringing about these processes often involve the enzyme-catalysed transfer of the phosphate group to intermediate substrates. Most ATP-mediated reactions require Mg2+ ions as cofactors.
ATP is regenerated by the rephosphorylation of AMP and ADP using the chemical energy obtained from the oxidation of food. This takes place during glycolysis and the Krebs cycle but, most significantly, is also a result of the reduction-oxidation reactions of the electron transport chain, which ultimately reduces molecular oxygen to water (oxidative phosphorylation).
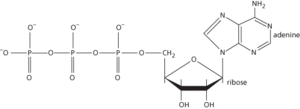
ATP
A nucleotide that is of fundamental importance as a carrier of chemical energy in all living organisms. It consists of adenine linked to d-ribose (i.e. adenosine); the d-ribose component bears three phosphate groups, linearly linked together by covalent bonds (see formula). These bonds can undergo hydrolysis to yield either a molecule of ADP (adenosine diphosphate) and inorganic phosphate or a molecule of AMP (adenosine monophosphate) and pyrophosphate (see atpase). Both these reactions yield a large amount of energy (about 30.6 kJ mol−1) that is used to bring about such biological processes as muscle contraction, the active transport of ions and molecules across plasma membranes, activation of proteins involved in signal transduction, and the synthesis of biomolecules. The reactions bringing about these processes often involve the enzyme-catalysed transfer of the phosphate group to intermediate substrates, for example by a kinase enzyme. Most ATP-mediated reactions require Mg2+ ions as cofactors.
ATP is regenerated by the rephosphorylation of AMP and ADP using the chemical energy obtained from the oxidation of food. This takes place during glycolysis and the Krebs cycle but, most significantly, is also a result of the reduction-oxidation reactions of the mitochondrial electron transport chain, which ultimately reduces molecular oxygen to water (oxidative phosphorylation). ATP is also formed by the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis.
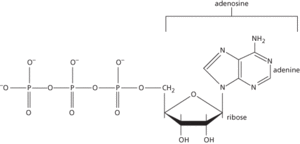
ATP
- voltage(symbol: V; unit: volt)
- voltage transformer
- voltaic cell
- voltaic pile
- Voltaire (1694–1778)
- voltameter
- volt-ampere(symbol: VA)
- volt efficiency
- Volterra integral equation
- voltmeter
- volt per metre
- volt(symbol: V)
- volume
- volume charge density
- volume compressor
- volume control
- volume diameter
- volume diffusion
- volume element
- volume index
- volume integral
- volume label
- volume lifetime
- volume limiter
- volumenometer