A test of the null hypothesis that a sample has been drawn from a normal distribution. An attractively simple test is that proposed by the Irish statistician Roy Geary in 1935. The Geary test compares the ratio of the mean deviation (see mean absolute deviation) divided by the standard deviation with the theoretical ratio for a normal distribution, which is . An alternative is the D'Agostino test suggested by D’Agostino in 1971. With ordered observations x(1)≤x(2)≤⋯≤x(n), the test statistic (see hypothesis test) is D, given by
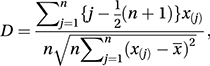 where x¯ is the sample mean. Special tables are required.
where x¯ is the sample mean. Special tables are required.Several more general tests of specified distributions have special cases for testing for normality. Examples include the Anderson–Darling test and the Shapiro–Wilk test. See also Cramér–von Mises test; Kolmogorov–Smirnov test.
- curve of growth
- curve sketching
- curvilinear coordinates
- curvilinear regression model
- curvilinear relation
- Curvolithus
- Curzon, George Nathaniel, 1st Marquis Curzon of Kedleston (1859–1925)
- Cush
- cusp
- cuspate foreland
- cusp cap
- cuspidate
- Custer, George (1839–76)
- custom
- customary units
- customer bounty
- customer data integration
- customer relationship management
- customer relationship management system
- customizable graphical user interface
- Customs and Excise
- customs and excise
- customs drawback
- customs duty
- custom software