Introduced by William Gosset in 1908, the t-distribution is the continuous probability distribution of a random variable formed from the ratio of a random variable with a standard normal distribution and the square root of a random variable with a chi-squared distribution divided by its degrees of freedom ν. Alternatively, it is formed from the square root of a random variable with an F-distribution in which the numerator has one degree of freedom. Its probability density function is
which gives the Cauchy distribution when ν = 1. The graph of f is similar in shape to a standard normal distribution, but is less peaked and has fatter tails. The distribution is used to test for significant differences between a sample mean and the population mean and can be used to test for differences between two sample means. The table gives, for different degrees of freedom, the values corresponding to certain values of α, to be used in a one-tailed or two-tailed t-test, as explained below.
α
2α
ν = 1
2
3
4
6
8
10
15
20
30
60
∞
0.05
0.10
6.34
2.92
2.35
2.13
1.94
1.86
1.81
1.75
1.72
1.70
1.67
1.64
0.025
0.05
12.71
4.30
3.18
2.78
2.45
2.31
2.23
2.13
2.09
2.04
2.00
1.96
0.01
0.02
31.82
6.96
4.54
3.75
3.14
2.90
2.76
2.60
2.53
2.46
2.39
2.33
0.005
0.01
63.66
9.92
5.84
4.60
3.71
3.36
3.17
2.95
2.84
2.75
2.66
2.58
Values for one- and two-tailed t-test
Corresponding to the first column value α, the table gives the one-tailed value tα,ν such that Pr(t > tα,ν) = α, for the t-distribution with ν degrees of freedom. Corresponding to the second column value 2α, the table gives the two-tailed value tα,ν such that Pr(|t| > tα,ν) = 2α. Interpolation may be used for values of ν not included.
The probability density function f for this distribution is given by
 where B is the beta function and ν is a positive parameter (usually an integer) known as the number of degrees of freedom. The distribution is symmetrical about its mode at 0, which is therefore (for ν > 1) also its mean. For ν > 2 the distribution has variance ν/(ν − 2).
where B is the beta function and ν is a positive parameter (usually an integer) known as the number of degrees of freedom. The distribution is symmetrical about its mode at 0, which is therefore (for ν > 1) also its mean. For ν > 2 the distribution has variance ν/(ν − 2).When ν=1 the distribution is a Cauchy distribution. As ν increases, the distribution increasingly resembles the standard normal distribution, which is its limit as ν → ∞. If X has a t-distribution with ν degrees of freedom, then X2 has an F-distribution with 1 and ν degrees of freedom. A t-distribution with ν degrees of freedom may be described as a tν-distribution.
The form of the distribution was published in 1908 by Gosset, writing under the pen-name ‘Student’, in the context of a random sample of size n from a population having a normal distribution. Gosset was finding the distribution of t, given by
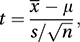 where μ is the population mean, and x¯ and s are, respectively, the sample mean and sample standard deviation with divisor (n−1). In Gosset's case ν=(n−1).
where μ is the population mean, and x¯ and s are, respectively, the sample mean and sample standard deviation with divisor (n−1). In Gosset's case ν=(n−1).The percentage points (see Appendix VI) of the t-distribution are used as critical values in carrying out a t-test (see hypothesis test) based on the value of t when μ is replaced by μ0, the value specified by the null hypothesis.
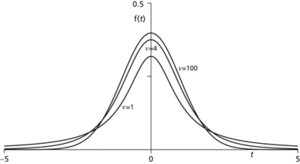
t-distribution. Distributions are illustrated for various values of the parameter ν and all have mean 0. The case ν=∞ corresponds to the normal distribution, and the case ν=1 corresponds to the Cauchy distribution. The chance of a very extreme value is greater for a t-distribution than for the normal distribution, but decreases as ν increases.
See Student’s t-distribution.
- EUI-48
- EUI-64
- Eukarya
- Eukaryota
- eukaryote
- Euler angles
- Euler characteristic
- Euler-Chelpin, Hans Karl August Simon von
- Euler cycle
- Euler force
- Eulerian current measurement
- Eulerian fluid dynamics
- Eulerian graph
- Eulerian trail
- Euler, Leonhard (1707–83)
- Euler line
- Euler-Maclaurin formula
- Euler multiplier
- Euler number
- Euler numbers
- Euler operators
- Euler pole
- Euler's constant
- Euler, Ulf Svante von
- Euler’s conjecture