The main organ of excretion and osmoregulation in vertebrates, through which nitrogenous waste material (usually in the form of urine) and surplus water, ions, etc., are eliminated from the body. In mammals there is a pair of kidneys situated in the abdomen (see illustration). Each has an outer cortex and an inner medulla and is made up of tubular units called nephrons, through which nitrogenous waste is filtered from the blood, with the formation of urine. The nephrons drain into a basin-like cavity in the kidney (the renal pelvis), which leads to the ureter and bladder.
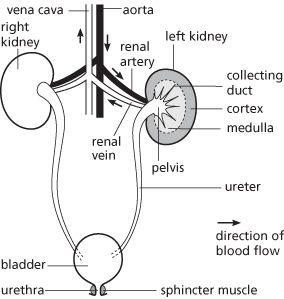
The kidneys of a mammal
- neutron excess
- neutron halo
- neutron interferometer
- neutron log
- neutron moisture meter
- neutron number
- neutron optics
- neutron scattering
- neutron soil-moisture probe
- neutron spin echo
- neutron star
- neutron temperature
- neutron–gamma sonde
- neutron–neutron sonde
- neutrophil
- Neville’s Cross, Battle of (17 October 1346)
- Nevilly, Treaty of
- New Academy
- New Australians
- Newcastle, Thomas Pelham-Holles, 1st Duke of (1693–1768)
- new classical economics
- Newcomb, Simon
- Newcomb, Simon (1835–1909)
- Newcomb’s paradox
- New Deal