A singular point which does not lie on the main curve of an equation but whose coordinates do satisfy the equation. For example, y2 = x2(x2−1) is not defined for −1<x<0, 0<x<1, but the function is defined for x = 0, and the point (0, 0) satisfies the equation. See figure.
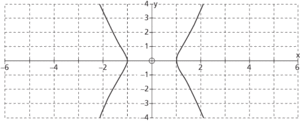
Curve with origin as an isolated point
- continuous wave
- continuous-wave radar
- continuum
- continuum hypothesis
- CONTOUR
- contour
- contour current
- contour diagram
- contour feathers
- contour integration
- contourites
- contour line
- contraception
- contract
- contractarianism
- contract curve
- contracted-out((services))
- contractible space
- contractile root
- contractile vacuole
- contracting Earth hypothesis
- contraction
- contractional kink band
- contraction((in animal physiology))
- contraction limit