A synonym for Newton’s method.
An algorithmic method for constructing a sequence of approximations to a root of an equation. Suppose it is desired to solve the equation f(x)=0 and that x1 is an approximate value for the root of the equation. If we write f′(xn) for the value of the derivative of f(x) (with respect to x) evaluated at the point x=xn, the sequence defined by
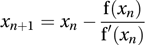 usually converges to a root of the equation. It is based on constructing the tangent to the curve y=f(x) at the point (xn, f(xn)), and taking xn+1 to be the x-coordinate of the point where this tangent cuts the x-axis.
usually converges to a root of the equation. It is based on constructing the tangent to the curve y=f(x) at the point (xn, f(xn)), and taking xn+1 to be the x-coordinate of the point where this tangent cuts the x-axis.
- Sunni
- sunrise
- sunseeker
- Sun sensor
- sunset
- sunshade
- sunshine recorder
- sunskirter
- sunspot
- sunspot cycle
- sunspot number
- sunspot theory
- Sun-synchronous orbit
- sun-tan age
- Sun Tsu
- Sunyaev–Zel'dovich effect
- sunyata
- Sun Yat-sen (1866–1925)
- Sunzi
- Suomi NPP
- sup
- super-
- superacid
- superadditive
- super-adiabatic lapse rate