See telescope.
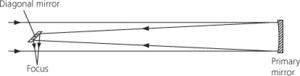
A reflecting telescope in which light is collected by a paraboloidal primary mirror and then reflected by a secondary mirror or prism within the tube to a focal point at the side of the tube, at right angles to the direction of view of the telescope. The image is inverted but not laterally reversed. The focal ratio should be larger than f/3, otherwise coma (see coma, optical) becomes excessive. The design was invented in 1668 by I. Newton.
- Portlandian
- portrait
- Port-Royal
- port scanning
- Portsmouth, Treaty of (1905)
- Portugal
- Portuguese empire
- Portuguese man-of-war
- POS
- poset
- POS expression
- Posidonius of Apamea (c.135–51)
- posit
- position
- positional astronomy
- positional cloning
- positional good
- positional information((in embryology))
- positionality
- positional system
- position angle
- position-angle effect
- position circle
- position-independent code
- positioning algorithm