Let E1, E2,…, En be n distinct events (see sample space). The probability that at least one occurs is P(E1 ⋃ E2 ⋃ … ⋃ En). The principle states that this can be expressed in terms of the probabilities of intersections as
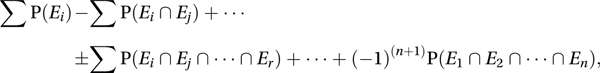 where the sums are over all combinations of different events.
where the sums are over all combinations of different events.
- eye candy
- eye lens
- eyelet-construction mica capacitor
- eye muscle
- eyepiece
- eye relief
- eyespot
- eye tooth
- eye tracking
- Eyharts, Léopold (1957– )
- eyot
- Eyring equation
- Eyring, Henry
- Eyring, Henry (1901–81)
- ezine
- Eötvös, Baron Lóránd von
- Eötvös effect
- E–isomer
- E–Z convention
- F
- f
- f0
- F0F1 complex
- F1
- F-1 engine