A method of reducing the variance of an estimate obtained via simulation. Suppose, for example, that we wish to estimate the quantity I, given by
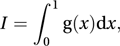 where g is a given function. An obvious method is to generate pseudo-random numbers u1, u2,…, un, in the interval (0, 1). Writing U1, U2,…, Un for the corresponding random variables, the estimator, I1, is given by
where g is a given function. An obvious method is to generate pseudo-random numbers u1, u2,…, un, in the interval (0, 1). Writing U1, U2,…, Un for the corresponding random variables, the estimator, I1, is given by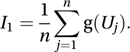 Importance sampling makes a more representative choice of values: suppose that f is a probability density function that resembles g in its general shape, and let F be the corresponding distribution function. Instead of working with U1, U2,…, Un, we work with V1, V2,…, Vn, where F(Vj)=Uj. The resulting estimator, I2, given by
Importance sampling makes a more representative choice of values: suppose that f is a probability density function that resembles g in its general shape, and let F be the corresponding distribution function. Instead of working with U1, U2,…, Un, we work with V1, V2,…, Vn, where F(Vj)=Uj. The resulting estimator, I2, given by will have a smaller variance than I1.
will have a smaller variance than I1.
- variable resistance gauge
- variable sharing property
- variable source areas
- variable star
- variable word length computer
- Variac
- variance
- variance, analysis of
- variance components model
- variance-ratio test
- variance reduction techniques
- variance–covariance matrix
- variant field
- variate
- variation
- variational method
- variational principle
- variation of latitude
- variegated capitalism
- variegation
- varies directly
- variety
- varimax rotation
- variogram
- variolitic