A node in a neural network.
An elongated branched cell that is the fundamental unit of the nervous system, being specialized for the conduction of impulses. A neuron consists of a cell body, containing the nucleus and Nissl granules; dendrites, which receive incoming impulses and pass them towards the cell body; and an axon, which conducts impulses away from the cell body, sometimes over long distances. Impulses are passed from one neuron to the next via synapses. Sensory neurons transmit information from receptors to the central nervous system. Motor neurons conduct information from the central nervous system to effectors (e.g. muscles). Interneurons form connections between neurons in the brain and ganglia, and play a key role in interpreting and analysing sensory information. (See illustration.) See also bipolar neuron; growth cone; multipolar neuron; neurite; unipolar neuron.
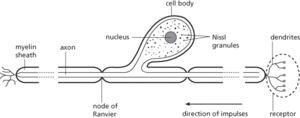
Sensory neuron
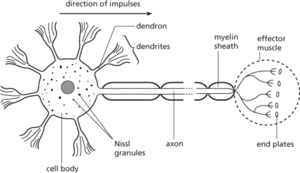
Motor neuron
- dissection
- dissection(of an interval)
- disseminated deposit
- dissepiment
- dissepimentarium
- dissimilarity
- dissimilarity index
- dissipation
- dissipation trail
- dissipative
- dissipative force
- dissipative system
- dissociation
- dissociation constant
- dissociation pressure
- Dissolution of the Monasteries
- dissolve
- dissolved load
- dissolved oxygen
- dissolved-oxygen level
- distal
- distal convoluted tubule
- distance
- distance between two codewords
- distance between two lines(in 3‐dimensional space)