A measurement of the skill of a forecast. The Priestley skill score, P, applies to value forecasts (such as forecasts of temperature). Let fi denote a forecast, and let oi denote the subsequent observed value, with o¯ denoting the mean of a set of n observed values. Then P is given by
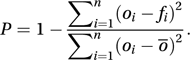 The Brier score was introduced in 1950 to assess the accuracy of probabilistic weather forecasts (e.g. ‘There is a probability pi of rain tomorrow’). Denoting the actual weather outcome by oi (equals 1 if the event occurs, and 0 if it does not) the Brier score, B, is given (for n forecasts) by
The Brier score was introduced in 1950 to assess the accuracy of probabilistic weather forecasts (e.g. ‘There is a probability pi of rain tomorrow’). Denoting the actual weather outcome by oi (equals 1 if the event occurs, and 0 if it does not) the Brier score, B, is given (for n forecasts) by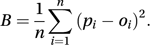 The smaller the value of B, the more skilful the forecasting procedure. If Bs denotes the Brier score for a standard forecasting system, then S, given by
The smaller the value of B, the more skilful the forecasting procedure. If Bs denotes the Brier score for a standard forecasting system, then S, given by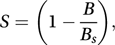 is called the Brier skill score.
is called the Brier skill score.
- time complexity
- time constant
- TIMED
- time delay
- time dependence of fundamental constants
- time deposit
- time dilation
- time discounting
- time discriminator
- time diversity
- time-division duplexing
- time-division multiple access
- time division multiplexing
- time-division multiplexing
- time division switch
- time-division switching
- time domain
- time domain reflectometer
- Time History of Events and Macroscale Interactions during Substorms
- time-homogeneous Markov chain
- time horizon
- time-inconsistency
- time lag
- time-lag argument
- time lags