Collections of objects or elements that have at least one characteristic in common. For example, the set X may consist of all the elements x1, x2, x3, etc. This is written {x1, x2, x3,…}=X. A specific element in a set is characterized by x1∈X, meaning x1 is a member of set X. A subset of set X, say M, would be written M⊂X, i.e. M is contained in X. If x3 is a member of both subsets M and N, then x3∈(M∩N), i.e. x3 belongs to the intersection of M and N. M∪N means the union of M and N. For example, if M consists of {1, 4, 5, 8} and N consists of {2, 3, 4, 5} then M∩N={4, 5} and M∪N={1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 8}. In the diagram, the rectangle represents the universal set E, circles represent sets or subsets. These diagrams are called Venn diagrams, after John Venn (1834–1923), who invented them.
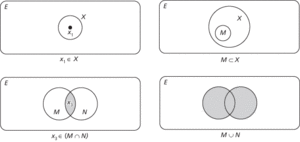
Sets.
- high electron mobility transistor
- High-Energy Astronomy Observatory
- High Energy Astrophysical Observatory
- high-energy astrophysics
- high-energy particle detector
- High-Energy Transient Explorer 2
- High-Energy Transient Explorer-2
- higher arithmetic
- higher derivative
- higher dimensions
- higher-order logic
- higher-order term
- higher‐order partial derivative
- highest common factor
- highest occupied molecular orbital
- high fidelity
- high-field-strength elements
- high frequency
- high-frequency resistance
- high-gain antenna
- high-inclination orbit
- Highland Clearances
- highlands, lunar
- high-level design
- high-level injection