A biological, chemical, or physical agent or situation that is reasonably likely, or has the potential, to cause illness or injury to humans, damage to property, damage to the environment, or some combination of these if it is not controlled. The product of the consequence and frequency of that situation occurring, hazards are associated with fire and explosion, pollution, chemical reactions, toxicity, mechanical failure, corrosion, and nuclear radiation. Hazards may arise due to the relaxation of management control, fatigue, carelessness, boredom and complacency, a loss or changes in operational knowledge, ageing and poorly maintained equipment, design modifications, and the abuse of trips. Hazards can be controlled through elimination, control of containment, and the controlled reduction in the likelihood or frequency and effect. They may be reduced through design standards, control of work, inspection, maintenance, safety reviews, control of ignition sources, use of detection devices, fireproofing, and effective operational and emergency response procedures.
1. A situation or event whose realization has the potential for damage to human life, society, the economy, or the environment. See also hazard and operability study.
2. A potential or actual malfunction of a logic circuit during change(s) of state of input variables. Hazards result from the nonideal behaviour of actual switching elements, e.g. noninstantaneous operation, turn-on time different from turn-off time.
In the UK the word hazard is sometimes used as the equivalent of race condition.
An error in the logic state of a logic circuit that causes or could cause the circuit to malfunction. Logic circuits require a finite time to operate and consequently introduce delays into the propagation of information. These delays are generally no more than a few microseconds, and for very high speed logic may be of the order of nanoseconds. These delays may invalidate the laws of Boolean algebra and cause errors in the logic state (see diagram).
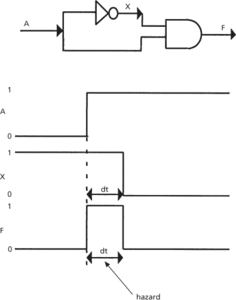
Hazard
An unexpected threat to humans and/or their property; a hazard includes both the event and its consequences. By this definition, the Indian monsoon is not a hazard, but its failure is. A natural event becomes a hazard through: the social processes which cause some people to be much more at risk from the effects of a hazard; a lack of options to minimize, or escape from, the effects of the hazard; the location of human settlement on potentially dangerous physical sites; the location of human settlement near potentially dangerous economic activity; and activities that aggravate events with natural causes.
‘As the range of hazards and vulnerabilities faced by any given community increases, it often becomes possible only to play one kind of risk off against another in search of a “less bad” scenario. Many highly vulnerable communities may deliberately choose to inhabit a hazard prone environment if this reduces other risks, related to income generation for example. Or, should they find themselves in hazard prone zones due to exclusion from formal land markets or for other reasons, they will many times opt to stay in order to maintain those conditions that provide them with the means to reduce daily life risk and vulnerability’ (UNDP Expert Group Meeting, Havana, 2002).
Hazard perception is the view which an individual has of a hazard. Robertson (1999) Geog. Rev. 89, 4 compares the reality of the tornado hazard with the portrayal in movies, finding the latter seriously misleading. Walker et al. (2002) Appl. Geog. 20, 2 report on the failure of regulatory practice to distinguish hazards from industrial accidents.
See cognitive dissonance.
- Yogacara
- Yohkoh
- yoke
- yoke mounting
- yolk
- yolk sac
- Yom Kippur War (1973)
- Yongle (1359–1424)
- Y organ
- Yorkist
- York, Richard Plantagenet, 3rd Duke of (1411–60)
- Yorkshire terrier
- Yorktown
- Yoruba empire of Oyo
- Yoshida Shigeru (1878–1967)
- yotta-
- Youden square
- Youden, William John (1900–71)
- Youden’s index
- Young, Brigham (1801–77)
- Young England
- Younger Dryas
- young fold mountain
- younging
- Young Ireland