A curve describing the growth of a population. Let y denote the size of the population at time t, with c denoting the ultimate size and b denoting the growth rate (the parameter that governs the rate at which the population approaches its maximum value). Simple two-parameter possibilities include
y = ce−e−bt
(the Gompertz equation)
y = c(1−e−bt)
(the Mitscherlich equation)
y = ct / (b+t)
(the Michaelis-Menten equation).
Taking reciprocals in the last of these gives the Lineweaver–Burk equation
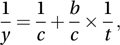 which is a simple linear model connecting 1/y and 1/t.
which is a simple linear model connecting 1/y and 1/t.A more general growth equation is the generalized logistic equation, also called the Richards equation:
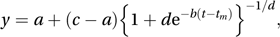 which describes growth from a low of a to a high of c, with tm being the time of maximum growth and d controlling whether that time occurs when the value of y is nearer to a or to c.
which describes growth from a low of a to a high of c, with tm being the time of maximum growth and d controlling whether that time occurs when the value of y is nearer to a or to c.
Used in biochemical engineering to describe and illustrate the evolution of biomass over time. These are plotted to illustrate the change of microbial cell concentration, either as dry weight or total population, over a period of time. Features of the batch cultivation of microorganisms show a lag phase in which the microorganisms adjust to the growth medium, an exponential growth phase as they rapidly multiply, a quiescence phase, and a death phase. A second growth curve may occur, known as diauxic or bi-phasic growth in which the microorganisms consume another nutrient, which may be an excreted product from the first phase such as ethanol. See limiting substrate.
A graph that records the changing isotopic levels of 207Pb, 206Pb, and 204Pb brought about by the radioactive decay of 238U, 235U, and 232Th. Very early in the Earth’s cooling history there was no radiogenic lead. With the passage of time radiogenic 206Pb, 207Pb, and 208Pb accumulated at the sites of uranium and thorium. The accumulation of radiogenic lead from an environment with constant ratios of U to Pb and Th to Pb would be expected to follow a simple growth curve, illustrating the increase of daughter isotopes with time. The curve would begin at the level of primordial lead and is normally plotted against axes of 207Pb:204Pb (y), and 206Pb:204Pb (x). The curve rises steeply at first, while more 207Pb than 206Pb is produced, but then flattens as 235U becomes depleted following its more rapid decay than that of 238U. Plotted in this way, the growth curve is the reverse of the decay curve. In reality, for any suite of samples, there would be a family of growth curves, each of which is specified by a particular value of the parameter 238U:204Pb. Each of these curves represents the course along which lead isotope ratios would evolve in a system presently containing a given 238U:204Pb ratio. As the equation governing these graphs is only a function of time, systems of the same age but different 238U:204Pb ratios will contain lead-isotope ratios lying along straight lines, known as isochrons. These isochrons will diverge from the assumed common lead-isotope ratio and will have slopes that are a function of age.
- turnkey operation
- turnkey project
- turnoff point
- turnover
- turnover rate
- turnover tax
- turnover time
- turnpike theorem
- turns ratio
- turns ratio(symbol: n)
- turnstile
- turnstone
- Turonian
- turpentine
- turquoise
- turreted
- turret tuner
- turriculate
- turtle
- turtle graphics
- Tutankhamun
- Tuthmosis I
- Tuthmosis III
- Tuttle–Giacobini–Kresák, Comet 41P/
- Tutu, Desmond (1931–2021)