A diagram that illustrates the relationship between two variables. It usually consists of two perpendicular axes, calibrated in the units of the variables and crossing at a point called the origin. Points are plotted in the spaces between the axes and the points are joined to form a curve. See also Cartesian coordinates; polar coordinates.
A number of vertices (or points or nodes), some of which are joined by edges. The edge joining the vertex U and the vertex V may be denoted by (U, V) or (V, U). The vertex‐set, that is, the set of vertices, of a graph G may be denoted by V(G) and the edge‐set by E(G). For example, the graph shown here on the left has V(G) = {U, V, W, X} and E(G) = {(U, V), (U, W), (V, W), (W, X)}.
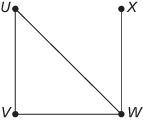
A graph
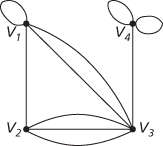
A multigraph
In general, a graph may have more than one edge joining a pair of vertices; when this occurs, these edges are called multiple edges. Also, a graph may have loops—a loop is an edge that joins a vertex to itself. In the other graph shown, there are 2 edges joining V1 and V3 and 3 edges joining V2 and V3; the graph also has three loops. See multigraph.
Normally, V(G) and E(G) are finite, but if this is not so, the result may also be called a graph, though some prefer to call this an infinite graph.
A graph consists of a set of nodes usually represented by small circles, and a set of arcs usually represented by lines. If a path can be found that connects all the nodes, then a graph is said to be a connected graph. If no pair of nodes is connected by more than one arc then the graph is said to be a simple graph. A graph in which each arc has an associated direction is a digraph.
A summary of the connections between the nodes of a graph is provided by an adjacency matrix. For a simple graph with n nodes, the entry in cell (i, j) of the n×n matrix will be 1 if nodes i and j are adjacent (i.e. directly connected), and 0 otherwise.
A diagram that presents the relationship between numbers or quantities. A graph is normally drawn with coordinate axes at right angles. They are used to display and illustrate the geometric relationship between data. The dependent variable is plotted on the x-axis while the independent variable is plotted on the y-axis.
1. A nonempty but finite set of vertices (or nodes) together with a set of edges that join pairs of distinct vertices. If an edge e joins vertices v1 and v2, then v1 and v2 are said to be incident with e and the vertices are said to be adjacent; e is the unordered pair (v1,v2).
A graph is usually depicted in a pictorial form in which the vertices appear as dots or other shapes, perhaps labelled for identification purposes, and the edges are shown as lines joining the appropriate points. If direction is added to each edge of a graph, a directed graph or digraph is obtained. The edges then form a finite set of ordered pairs of distinct vertices, and are often called arcs. In the pictorial representation, arrows can be placed on each edge. With no direction specified, the graph is said to be undirected.
Although helpful visually these representations are not suitable for manipulation by computer. More useful representations use an incidence matrix or an adjacency matrix.
Graphs are used in a wide variety of ways in computing: the vertices will usually represent objects of some kind and the edges will represent connections of a physical or logical nature between the vertices. So graphs can be used to model in a mathematical fashion such diverse items as a computer and all its attached peripherals, a network of computers, parse trees, logical dependencies between subroutines or nonterminals in a grammar, VLSI diagrams, related items in databases for molecules and reaction networks (for chemoinformatics and bioinformatics). Trees and lists are special kinds of graphs.
Variations exist in the definition of a graph. There is some dispute about whether one edge can join a vertex to itself, whether empty sets are involved, whether an infinite number of vertices and edges are permitted, and so on.
See also connected graph, network, weighted graph.
2. (of a function f) The set of all ordered pairs (x,y) with the property that y = f(x). Often such a graph is represented by a curve.
- induced polarization
- induced potential
- induced pulsed transient
- induced radioactivity
- inducer
- inducible nitric oxide synthase
- inductance
- induction
- induction by elimination
- induction by enumeration
- induction coil
- induction compass
- induction flowmeter
- induction heating
- induction instrument
- induction log
- induction, mathematical
- induction microphone
- induction motor
- induction sonde
- inductive
- inductive coupling
- inductive effect
- inductive feedback
- inductive interference