An experimental design in which the variables have an implicit hierarchy. For example, a hospital has two wings (I and II). Patients in wing I are randomly assigned to either consultant A or consultant B. Patients in wing II are randomly assigned to either consultant C or consultant D. Thus consultants A and B are nested within the wing I patients, and consultants C and D are nested within the wing II
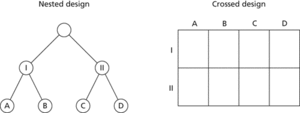
Nested design. The figure illustrates the difference between nested and crossed designs; in the latter, every combination of the crossed variables occurs.
patients. If, instead, all the patients in the hospital had been randomly assigned to one of the four consultants then this would have been a crossed design.
- Wold’s decomposition theorem
- Wolf 359
- Wolfcampian
- Wolf, David Alexander (1956– )
- Wolf diagram
- Wolfe, James (1727–59)
- Wolff, Christian (1679–1754)
- wolffish
- Wolff–Kishner reduction
- Wolff’s law
- Wolf, (Johann) Rudolf (1816–93)
- Wolf, Maximilian (‘Max’) Franz Joseph Cornelius (1863–1932)
- Wolfowitz, Jacob (1910–81)
- Wolf Prize
- wolfram
- wolframite
- Wolf sunspot number
- Wolf–Lundmark–Melotte system
- Wolf–Rayet star
- wollastonite
- Wollaston prism
- Wollaston, William (1660–1724)
- Wollaston, William Hyde
- Wollaston wire
- Wollstonecraft, Mary (1759–97)