A device used to detect and measure ionizing radiation. It consists of a tube containing a low-pressure gas (usually a mixture of methane with argon or neon) and a cylindrical hollow cathode, through the centre of which runs a fine-wire anode. A potential difference of about 1000 volts is maintained between the electrodes. An ionizing particle or photon passing through a window into the tube will cause an ion to be produced and the high p.d. will accelerate it towards its appropriate electrode, causing an avalanche of further ionizations by collision. The consequent current pulses can be counted in electronic circuits or simply amplified to work a small loudspeaker in the instrument. It was first devised in 1908 by Hans Geiger. Geiger and Walther Müller produced an improved design in 1928.
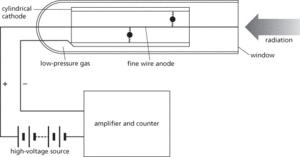
Geiger counter.
A device used to detect and measure ionizing radiation. It consists of a tube containing a low-pressure gas (usually argon or neon with methane) and a cylindrical hollow cathode through the centre of which runs a fine-wire anode. A potential difference of about 1000 volts is maintained between the electrodes. An ionizing particle or photon passing through a window into the tube will cause an ion to be produced and the high p.d. will accelerate it towards its appropriate electrode, causing an avalanche of further ionizations by collision. The consequent current pulses can be counted in electronic circuits or simply amplified to work a small loudspeaker in the instrument. It was first devised in 1908 by the German physicist Hans Geiger (1882–1945). Geiger and Walther Müller (1905–79) produced an improved design in 1928.
A gas-filled tube that is used to detect ionizing radiation, especially alpha particles, and to count particles. It contains a low-pressure gas and has a thin wire anode mounted coaxially inside a cylindrical cathode with a potential difference, slightly lower than that required to produce a discharge, maintained across the electrodes. When radiation enters through a thin window the gas along its path becomes ionized. The ions are accelerated by the field and produce an avalanche, which is quickly quenched. The resulting current pulse is amplified and registered by a detector (typically a loudspeaker) or a counting device.
The output is substantially constant for a wide range of voltage; this is the operating region of the tube. The tube is also independent of the energy of the incident radiation in this region.
http://vega.org.uk/video/programme/196 A short video demonstration of a Geiger counter
See geiger–müller counter.
- Wilson cycle
- Wilson, Edmund Beecher
- Wilson, Edward O. (1929)
- Wilson, Edward Osborne
- Wilson, Edwin Bidwell (1879–1964)
- Wilson effect
- Wilson, Harold (1916–95)
- Wilson, John Tuzo
- Wilson, John Tuzo (1908–93)
- coefficient of determination
- coefficient of discharge
- coefficient of expansion
- coefficient of friction
- coefficient of localization
- coefficient of nivosity
- coefficient of performance
- coefficient of restitution
- coefficient of skewness
- coefficient of sliding friction
- coefficient of variation
- coefficient of volumetric expansion
- coelacanth
- Coelacanthiformes
- Coelenterata
- coelenterate