An inhibitory neurotransmitter in the central nervous system (principally the brain) that is capable of increasing the permeability of postsynaptic membranes. GABA is synthesized by decarboxylation of the amino acid glutamate.
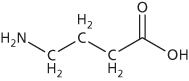
Gamma-aminobutyric acid
An inhibitory neurotransmitter in the central nervous system (principally the brain) that is capable of increasing the permeability of postsynaptic membranes to chloride ions (see inhibitory postsynaptic potential). GABA is synthesized by decarboxylation of the amino acid glutamate. There are three classes of GABA receptors: GABAA and GABAC receptors are ionotropic receptors whereas GABAB receptors are metabotropic receptors. In crustaceans and annelids, GABA is an inhibitory transmitter at synapses influencing muscle activity. Benzodiazepine drugs, such as valium, exert their anti-anxiety effect by allosterically binding to GABAA receptors and enhancing the action of GABA.
- Pinkie, Battle of (10 September 1547)
- pinna
- pinnacle reef
- pinnate fractures
- pinnular plates
- pinnules
- Pinochet Ugarto, Augusto (1915–2006)
- pinocytosis
- pinout
- PIN photodiode
- Pinus longaeva
- Pinwheel Galaxy
- PIO
- PIOCW
- pion
- Pioneer
- pioneer community
- Pioneer Venus
- pi orbital
- pipe
- pipe chase
- pipefish
- pipeline
- pipeline processing
- pipelining