A system of food chains that are linked with one another. In a food web a particular organism may feed at more than one trophic level. For example, in a pond food web a freshwater mussel may feed directly on green algae, in which case it is a primary consumer. However, it can also feed on protozoa, which are themselves primary consumers, in which case the mussel is the secondary consumer. A food web does not usually include the decomposers, but these organisms are very important in the flow of energy through a food web (see energy flow).
A series of interconnected and overlapping food chains in an ecosystem. A small change in the number of species in a food web can have consequences both for community structure and ecosystem processes (Emmerson et al. (2005) Glob. Change Biol. 11, 3).
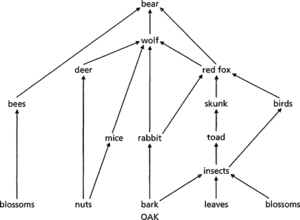
Food web
- unconditional statement
- unconfined aquifer
- unconfined compressive strength
- unconfined vapour cloud explosion
- unconfirmed service
- unconformity
- unconformity trap
- unconformity-type uranium ore
- unconscious
- unconsolidated
- uncontrolled format string
- uncorrected moment
- uncorrelated variables
- uncountable
- uncoupling protein
- uncovered interest parity
- UNCTAD
- undae
- undaform
- undated security
- undathem
- undecidability
- undecidable
- undepleted mantle
- under-capitalized