See modulation.
A form of modulation in which pulses are used to modulate the carrier wave or, more commonly, in which a pulse train is used as the carrier (the pulse carrier). Information is conveyed by modulating some parameter of the pulses with a set of discrete instantaneous samples of the message signal. The minimum sampling frequency is the minimum frequency at which the modulating waveform can be sampled to provide the set of discrete values without a significant loss of information.
Different forms of pulse modulation are shown in Fig. a. In pulse-amplitude modulation (PAM), the amplitude of the pulses is modulated by the corresponding samples of the modulating wave. In pulse-time modulation (PTM), the samples are used to vary the time of occurrence of some parameter of the pulses. Particular forms of pulse-time modulation are pulse-duration modulation (PDM), also known as pulse-length modulation (PLM) or pulse-width modulation (PWM), in which the time of occurrence of the leading edge or trailing edge is varied from its unmodulated position, pulse-frequency modulation (PFM), in which the pulse repetition frequency of the carrier pulses is varied from its unmodulated value, and pulse-position modulation (PPM), in which the time of occurrence of a pulse is modulated from its unmodulated time of occurrence, i.e. the pulse repetition period is varied. All these types of pulse modulation are examples of uncoded modulation.
• Pulse code modulation (PCM) is a form of digital modulation: only certain discrete values are allowed for the modulating signals. The modulating signal is sampled, as in other forms of pulse modulation, but any sample falling within a specified range of values is assigned a discrete value. Each value is assigned a pattern of pulses and the signal transmitted by means of this code. There are a number of variations on the way in which this code is transmitted, including NRZ (nonreturn to zero) PCM, RZ (return to zero) PCM, return to zero AMI (alternate mark inversion), and biphase PCM, also called Manchester code. These different schemes are shown in Fig. b. The electronic circuit or device that produces the coded pulse train from the modulating waveform is termed a coder (or pulse coder). A suitable decoder must be used at the receiver in order to extract the original information from the transmitted pulse train. Morse code is a very well known example of a pulse code.
• Delta modulation (DM), also called slope modulation, is another form of digital modulation in which the transmitted information only indicates whether the signal to be transmitted has been encoded to have a rising or falling transition. The simplest form is linear delta modulation (LDM), in which just two levels are used for quantization. This can therefore be encoded using one bit. The levels chosen are critical. If they are too small, the modulation process cannot keep up with slope variations in the input signal, a condition referred to as slope overload. If the levels are too large, the system can suffer from granular noise as the output oscillates around the target value of the input waveform. Adaptive delta modulation (ADM) and continuously variable slope delta modulation (CVSD) are techniques designed to improve the granular noise and slope overload performance of a delta modulation system by making use of quantization levels that are changed dynamically by matching them to the slope of the input waveform. The difference between them is in the detail of how the levels are varied.
Pulse modulation is commonly used for time-division multiplexing.
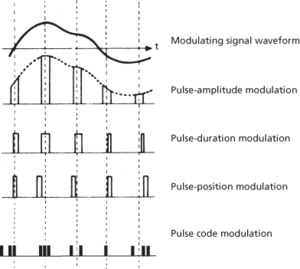
(a) Forms of pulse modulation
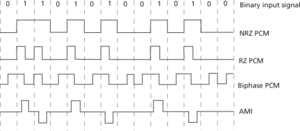
(b) Forms of pulse code modulation
- JOIDES
- join operator
- joint
- joint costs
- joint cumulative distribution function
- joint distribution
- Joint Electronic Device Engineering Council
- joint independence
- Joint Oceanographic Institutions for Deep Earth Sampling
- Joint Photographic Experts Group
- Joint Polar Satellite System-1
- joint probability
- joint probability density function
- joint probability distribution
- joint probability mass function
- joint production
- joint profit maximization
- joint set
- joint-stock bank
- joint-stock company
- joint supply
- joint system
- joint venture
- Joinville, Jean de (1224–1317)
- Joliot-Curie, Frédéric