A device used in cathode-ray tubes (including television tubes), electron microscopes, etc., to produce a steady narrow beam of electrons. It usually consists of a heated cathode, control grid, and two or more annular anodes inserted in an evacuated tube. The electrons emitted by the cathode are attracted to the final anode, through which they pass. The intensity of the beam is regulated by the control grid and potential differences between the anodes create electric fields that focus the diverging electrons into a narrow beam.
A device that produces an electron beam and forms an essential part of many instruments, such as cathode-ray tubes, electron microscopes, and linear accelerators, all of which need electron beams for their operation. The source of electrons may be a thermionic cathode, as shown in the diagram, or a field emitter. A series of accelerating and focusing electrodes usually produces a narrow beam of high-velocity electrons.
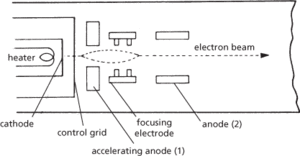
Electron gun
- harmonic mean
- harmonic motion
- harmonic number
- harmonic oscillator
- secondary crushing
- secondary depressions
- secondary electron
- secondary emission
- secondary enrichment
- secondary failure
- secondary front
- secondary geochemical differentiation
- secondary geochemical dispersion
- secondary growth
- secondary immunological response
- secondary index
- secondary industry
- secondary-ion mass spectrometry
- secondary-ion mass spectroscopy
- secondary market
- secondary matrix
- secondary memory
- secondary metabolite
- secondary migration
- secondary mineral