The diameter of a pipe that gives the minimum overall cost for any specific rate of flow of a fluid (see Fig. 19). The total costs of a pipe comprise the capital and operating costs. The capital cost increases with pipe diameter while the operating costs decrease with increasing diameter since the pumping costs to overcome frictional pressure resistance decreases. Where the cost can be related to diameter, the economic pipe diameter can be found mathematically as the turning point by differentiating the total cost with respect to diameter.
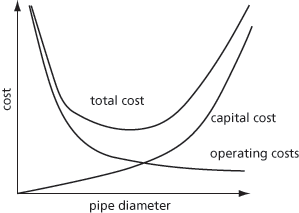
Fig. 19
- mamma
- Mammalia
- mammal-like reptiles
- mammary glands
- mammatus
- mammillary
- mammillated
- mammillated topography
- Mammoth
- mammoth
- Mammuthus
- Mammutidae
- MA model
- MAN
- managed currency
- managed data network service
- binormal
- bin packing problem
- bin-packing problem
- bio-
- bioaccumulation
- bioactivation
- bioarchaeology
- bioassay
- biocapacity