The gas that surrounds the earth. The composition of dry air at sea level is: nitrogen 78.08%, oxygen 20.95%, argon 0.93%, carbon dioxide 0.03%, neon 0.0018%, helium 0.0005%, krypton 0.0001%, and xenon 0.00001%. In addition to water vapour, air in some localities contains sulphur compounds, hydrogen peroxide, hydrocarbons, and dust particles.
The lowest level of the atmosphere, in which most of the weather occurs, is called the troposphere. Its thickness varies from about 7 km at the poles to 28 km at the equator and in this layer temperature falls with increasing height. The next layer is the stratosphere, which goes up to about 50 km. Here the temperature remains approximately constant. Above this is the ionosphere, which extends to about 1000 km, with the temperature rising and the composition changing substantially. At about 100 km and above most of the oxygen has dissociated into atoms; at above 150 km the percentage of nitrogen has dropped to nil. In the ionosphere the gases are ionized by the absorption of solar radiation. This enables radio transmissions to be made round the curved surface of the earth as the ionized gas acts as a reflector for certain wavelengths. The ionosphere is divided into three layers. The D-layer (50–90 km) contains a low concentration of free electrons and reflects low-frequency radio waves. The E-layer (90–150 km) is also called the Heaviside layer or Heaviside–Kennelly layer as its existence was predicted independently by Oliver Heaviside (1850–1925) and Arthur E. Kennelly (1861–1939). This layer reflects medium-frequency waves. The F-layer (150–1000 km) is also called the Appleton layer after its discoverer Sir Edward Appleton (1892–1965). It has the highest concentration of free electrons and is the most useful for radio transmission. Wavelengths between 8 mm and 20 m are not reflected by the ionosphere but escape into space. Therefore television transmissions, which utilize this range, require artificial satellites for reflection (or reception, amplification, and retransmission). From about 400 km, the outermost region of the atmosphere is also called the exosphere.
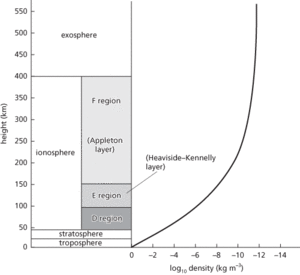
Earth’s atmosphere.
The gas that surrounds the earth. The composition of dry air at sea level is: nitrogen 78.08%, oxygen 20.95%, argon 0.93%, carbon dioxide 0.03%, neon 0.0018%, helium 0.0005%, krypton 0.0001%, and xenon 0.00001%. In addition to water vapour, air in some localities contains sulphur compounds, hydrogen peroxide, hydrocarbons, and dust particles.
- volcanic plug
- Volcanic units
- volcanism
- volcano
- volcano-tectonic depression
- vole
- Volgian
- volition
- volonté générale, volonté de tous
- Volstead Act (1919)
- volt
- Volta, Alessandro Giuseppe Antonio Anastasio (1745–1827)
- Volta, Count Alessandro Giuseppe Antonio Anastasio
- voltage
- voltage amplifier
- voltage between lines
- voltage clamp
- voltage-controlled amplifier
- voltage-controlled current source
- voltage-controlled voltage source
- voltage divider
- voltage doubler
- voltage drop
- voltage feedback
- voltage gain