An instrument used to obtain the rheological properties of fluids. It consists of a fixed flat surface with another rotating surface held at a fixed elevation above, with a sample of the fluid sandwiched between them (see Fig. 33). The rotational speed and distance defines the shear rate. The torque to resist the motion defines the characteristic shear rate. The apparent viscosity is calculated from the ratio of the shear stress to shear rate. The surface can be heated or cooled to determine the rheological properties as a function of temperature.
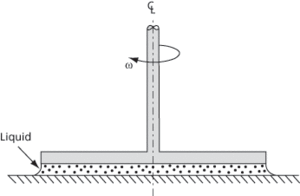
Fig. 33
- bearer
- bearer bond
- bearer network
- bearing
- bearing capacity
- bear market
- beat Cepheid
- beats
- Beattie, James (1735–1803)
- Beattie–Bridgman equation
- Beaufort
- Beaufort scale
- Beaufort, Sir Francis
- Beaumont, (Jean Baptiste Armand Léonce) Elie de
- Beauregard, Pierre Gustave Toutant (1818–93)
- beauty
- Beauvoir, Simone de (1908–86)
- beaver
- Beaverbrook, William Maxwell Aitken, Baron (1879–1964)
- Beccaria, Cesare (1738–94)
- Beche, Henry Thomas de la (1796–1855)
- Becher process
- Beche, Sir Henry Thomas de la
- Bechuanaland
- Becke, Friedrich Johann Karl (1855–1931)