The sensory part of the cochlea in the inner ear, which responds to sound. This organ, named after Italian anatomist A. G. G. Corti (1822–88), projects into the cochlear duct and consists of two membranes that run parallel to each other: sensory hair cells, rooted in the basilar membrane, are in contact with the overlying tectorial membrane (see illustration). During the transmission of sound waves the basilar membrane vibrates, causing the sensory hairs to flex against the tectorial membrane; this results in the production of impulses, which are transmitted to the brain via the auditory nerve.
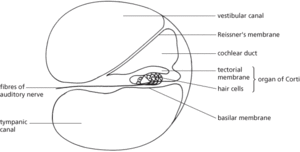
Organ of Corti (vertical section through one turn of the cochlea)
- Huygens probe
- Huygens’ construction
- Huygens’ principle
- Huynh–Feldt correction
- HVAC
- H wave
- HWHM
- HX
- HY-1B
- hyacinth
- Hyades
- Hyaenidae
- Hyakutake
- Hyakutake, Comet
- hyaline
- hyaline cartilage
- hyaloclastite
- hyalopilitic
- hyaloplasm
- Hyalospongea
- hyaluronic acid
- hyaluronidase
- hybrid
- hybrid broadcast broadband TV
- hybrid capitalism