1. (in physics) An interaction between two different parts of a system or between two or more systems. Examples of coupling in the spectra of atoms and nuclei are Russell–Saunders coupling, j-j coupling, and spin–orbit coupling. In the spectra of molecules there are five idealized ways (called the Hund coupling cases) in which the different types of angular momentum in a molecule (the electron orbital angular momentum L, the electron spin angular momentum S, and the angular momentum of nuclear rotation N) couple to form a resultant angular momentum J. (In practice, the coupling for many molecules is intermediate between Hund’s cases due to interactions, which are ignored in the idealized cases.) In solid-state physics an example of coupling is electron–phonon coupling, the analysis of which gives the theories of electrical conductivity and superconductivity. See also coupling constant.
2. (in chemistry) A type of chemical reaction in which two molecules join together; for example, the formation of an azo compound by coupling of a diazonium ion with a benzene ring.
1. An interaction between two different parts of a system or between two or more systems. Examples of coupling in the spectra of atoms and nuclei are Russell-Saunders coupling, j-j coupling, and spin–orbit coupling. In the spectra of molecules there are five idealized ways (called the Hund coupling cases) in which the different types of angular momentum in a molecule (the electron orbital angular momentum L, the electron spin angular momentum S, and the angular momentum of nuclear rotation N) couple to form a resultant angular momentum J. (In practice, the coupling for many molecules is intermediate between Hund’s cases due to interactions, which are ignored in the idealized cases.)
2. A type of chemical reaction in which two molecules join together; for example, the formation of an azo compound by coupling of a diazonium ion with a benzene ring.
A measure of the strength of interconnections between modules of a program. A high coupling would indicate strong dependencies between one module and another. Loose coupling allows greater flexibility in the design and better traceability, isolation, and correction of faults. The strength of coupling depends on the number of references of one module by another, the amount of data passed (or shared) between modules, the complexity of the interface between modules, and the amount of control exercised by one module over another. Completely decoupled modules have no common data and no control flow interaction. See also cohesion, coupled.
The interaction between two circuits so that energy is transferred from one to the other. In common-impedance coupling there is an impedance common to both circuits (Figs. a, b).
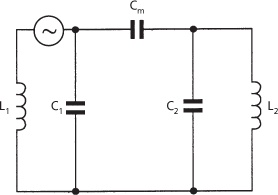
(a) Capacitive coupling
(b) Inductive coupling
The impedance may be a capacitance (capacitive coupling), a capacitance and a resistance (resistance-capacitance coupling), an inductance (inductive coupling), or a resistance (direct coupling). The impedance may be a part of each circuit or connected between the circuits. In mutual-inductance coupling the circuits are coupled by the mutual inductance, M, between the coils L1 and L2 (Fig. c). The coils used are often those of a transformer. The use of two separate coils between amplifier stages rather than a transformer is termed choke coupling. Mixed coupling is a combination of mutual-inductance coupling and common-impedance coupling.
The coupling coefficient, K, is defined as
where Xm is the reactance common to both circuits and X1 and X2 are the total reactances, of the same type as Xm, of the two circuits. For Fig. a:
For Fig. b:
For Fig. c:
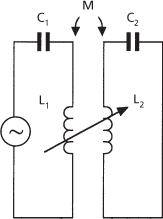
(c) Mutual-inductance coupling
The current in the secondary circuit depends on the degree of coupling and the frequency. Critical coupling occurs when KQ = 1, where Q is the Q factor of the circuit. A single peak occurs at the resonant frequency of the circuit and the current has its optimum value. Overcoupling occurs when K > 1/Q; the current has two side peaks with a dip at the resonant frequency. Undercoupling, when K < 1/Q, produces a smaller central peak than the optimum.
Band-pass filters often employ overcoupling, in order to pass a narrow band of frequencies, followed by undercoupling, to compensate for the central dip. In a tuned circuit, the bandwidth passed varies with frequency. This may be overcome by employing mixed coupling using a capacitance with the mutual inductance to give a constant bandwidth for a range of frequencies.
Cross coupling is unwanted coupling between communication channels, circuits, or components, particularly those with a common power supply. The removal of unwanted signals, especially those due to cross coupling, is called decoupling. It is usually achieved using a series inductance or a shunt capacitor
The connectivity within the components of a system. For example, the physics, chemistry, and biology of the ocean are coupled since the oceanic CO2 cycle is controlled by the ocean circulation, the supply of sunlight, and major and trace nutrients delivered by the oceanic and atmospheric circulation. Strong couplings link human dynamics, biology, biochemistry, geochemistry, geology, hydrology, and geomorphology; see Barry et al. (2009) Geomorph 103, 3, 496. Coupling behaviour conditions the way a system responds to disturbance, and is therefore important in determining the response to human-induced, climatically induced, or tectonically induced environmental change. See Harvey, (2002) Geomorph. 44, 3–4, 175 on coupling within a fluvial system, and Tulaczyk in D. M. Mickelson and J. W. Attig, eds (1999) considers coupling between ice and till at the glacier bed.
- Palestine
- Palestine Liberation Organization
- palette
- Paley, William (1743–1805)
- palimpsest
- palindromic
- palingenesis
- palinspastic map
- palisade
- palladium
- Pallas
- pallasite
- Pallava
- pallet
- pallial line
- pallial sinus
- pallium
- Pall ring
- Palmachim Spaceport
- Palmer Drought Severity Index
- Palmer method
- Palmerston, Henry John Temple, 3rd Viscount (1784–1865)
- palmitate
- palmitic acid
- palmtop computer