A circuit or device that produces an output voltage that is substantially constant and independent of variations either in the input voltage or in the load current, i.e. it acts as a constant-voltage source. Such a device is most often used as a voltage regulator.
An early form of voltage stabilizer was based on the gas-discharge tube. Such circuits have now largely been superseded by circuits based on solid-state devices, such as the Zener diode (Fig. a) or the bipolar junction transistor (Fig. b). In the series stabilization circuit shown in Fig. b the load impedance is in series with the circuit.
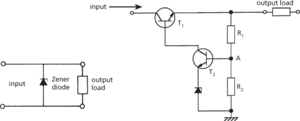
(a) Zener diode stabilizer circuit (b) Series stabilizer circuit
- stream cipher
- streamer
- stream flood
- streamflow
- stream function
- stream gauge
- stream grade
- streaming
- streaming audio
- streaming media
- streaming potential
- streaming tape transport
- streaming technology
- streaming video
- streamline
- streamline flow
- stream of consciousness
- stream order
- stream power
- stream-sediment analysis
- streamsink
- streams interface
- stream table
- stream terrace
- stream transformer