For a random variable X the rth moment (about the origin) is defined to be the expected value of Xr, where r is a non-negative integer. It is usually denoted by μ′r. So μ′0=1 and μ′1=μ, the mean of X.
The rth moment about the mean (or central moment or corrected moment) is defined to be the expected value of (X−μ)r and is usually denoted by μr. Thus μ1=0 and μ2=σ2, the variance of X. The moments about the mean can be expressed as linear combinations of the uncorrected moments, for example:
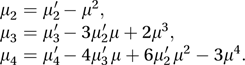 Either set of moments can also be expressed in terms of linear combinations of simple functions of the cumulants. It should be noted that, for some distributions, μr′ and μr may exist only for small values of r.
Either set of moments can also be expressed in terms of linear combinations of simple functions of the cumulants. It should be noted that, for some distributions, μr′ and μr may exist only for small values of r.