A fluid body tissue that acts as a transport and homeostatic medium within an animal. It is contained within a blood vascular system and in vertebrates is circulated by means of contractions of the heart. Oxygen and nutrients are carried to tissues, and carbon dioxide and chemical (nitrogenous) waste are transported from tissues to excretory organs for disposal (excretion). In addition blood carries hormones, acts as a defence system, and is important in maintaining a suitable osmotic and pH environment for tissues. Blood consists of a liquid (see blood plasma) containing blood cells (see erythrocyte; leucocyte) and platelets.
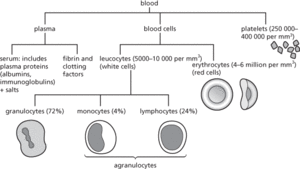
Composition of mammalian blood
- character machine
- character mode
- character recognition
- character representation
- character set
- character states
- character string
- character table
- character type
- chara marl
- charcoal
- Charcot, Jean-Martin
- Chargaff, Erwin
- Chargaff, Erwin (1905–2002)
- Chargaff’s rule
- charge
- chargeability
- charge back
- charge carrier
- charge conjugation
- charge-coupled device
- charged-body potential method
- charge density
- charge density wave
- charge hand