A geometrical representation of a two-state system in quantum mechanics in which the system is represented by a sphere. An example of a quantum-mechanical system that can be represented in this way is the spin of an electron, with the two states in this case being spin-up and spin-down. The spin-up and spin-down states are antipodal points on the sphere, with one of them being the north pole and the other the south pole. The Bloch sphere was introduced by Felix Bloch in 1946.
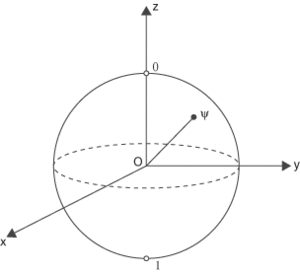
Bloch sphere. Any quantum state Ψ of a two-level system can be represented as a point on the surface of a Bloch sphere.
- citric-acid cycle
- citrine
- citta-matra
- City
- city
- city-block metric
- City Code
- city marketing
- city network
- city of refuge
- city region
- city-size distribution
- city/state relations
- civet
- civil disobedience
- Civil Rights Acts (1866)
- civil society
- civil time
- civil twilight
- Civil War, English
- civil wars, French
- civil wars, Roman
- civil year
- CIX
- Cixi (1834–1908)