A polygon with three vertices. As demonstrated in the first figure, the angles of a triangle ABC add up to 180°. By considering separate areas, illustrated in the second figure, the area of the triangle equals ‘half base times height’.
If now A, B, and C denote the angles of the triangle, and a, b, and c the lengths of the sides opposite them, the following results hold:
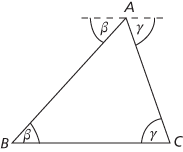
Proving the angle sum formula
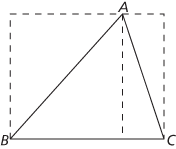
Determining the area of a triangle
(i) The area of the triangle equals .
(ii) The sine rule:
where R is the radius of the circumcircle.
(iii) The cosine rule:
(iv) The tangent rule:
(v) Hero’s formula: Let . Then the area of the triangle equals
See acute, obtuse, oblique, equilateral, isosceles triangle, right-angled triangle, scalene triangle, solution of triangles, spherical triangle.
- a.e.
- aeciospore
- aedifichnia
- Aegean civilization
- aegirine
- Aegospotami, Battle of
- Aegyptopithecus zeuxis
- Aelita
- AEM-2
- Aeneas
- Aenesidemus of Cnossos (1st)
- aeolian
- aeolian abrasion
- aeolianite
- aeolian processes
- aeolian ripple
- aeolian soil
- Aeolis Quadrangle
- Aeolus
- aeon
- aeration
- aeration number
- aeration zone
- aerial
- aerial photograph