A theorem published in 1941 that concerns the distribution of the mean, X̄, of n independent identically distributed random variables, X1, X2,…, Xn. The theorem requires that the expected values of Xj, Xj2, and | Xj |3 are finite and equal to 0, σ2, and τ, respectively for all j. Denoting the distribution function of the standard normal distribution by Φ, the theorem states that there is a value c for which
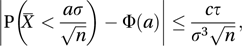 for all a. The value of c is known to be less than 0.475.
for all a. The value of c is known to be less than 0.475.
- Aratauran
- Arbenz Guzmán, Jacobo (1913–71)
- Arber, Werner
- arbitrage
- arbitrage pricing theory
- arbitrageur
- arbitrarily large/small
- arbitrary
- arbitrary constant
- arbitrary unit
- arbitration
- arborescent
- arbovirus
- arbuscular mycorrhiza
- Arbuthnot, John (1667–1735)
- arc
- arc-connected
- arccos
- arccosh
- arc discharge
- arc elasticity
- Arcesilaus (c.316–242)
- arch
- archae-
- Archaea