For two events A and B, the probability that A occurs, given that B has occurred, is denoted by Pr(A | B), read as ‘the probability of A given B’. This is called a conditional probability. Provided that Pr(B) > 0, Pr(A | B) = Pr(A ∩ B)/Pr(B). If A and B are independent events, Pr(A|B) = Pr(A), which rearranges to the product law for independent events: Pr(A ∩ B) = Pr(A) Pr(B).
If A and B are events (see sample space), and P(B)>0, the conditional probability of A given B is defined by
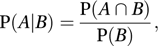 or equivalently
or equivalently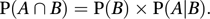
If P(A)>0 also, then P(A ∩ B)=P(A)×P(B|A), so
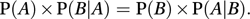
The ‘A|B’ notation was introduced by Jeffreys and popularized by Feller. See also bayes's theorem; independent events.
Term for the probability of one event given, or conditional upon another. In the standard mathematical development the conditional probability of B upon A is defined as the ratio of the probability of (A & B) to the probability of A, although there exist reasons for taking it as primitive, as has been done by Keynes and Popper (because a subject may be willing to ascribe a definite value to the conditional probability, when still very uncertain about the actual probability of (A & B) and about the probability of A). The process of conditionalizing is one of taking the probability of an event e′ occurring after another event e has occurred, to have the value that the conditional probability of e′ upon e was, before e occurred. Personalist theories of probability justify the process as required by coherence over time. The view that the process is central to rational belief formation and modification is characteristic of the Bayesian school of statistics. See also Adams’s thesis, Dutch book.
- cassowary
- cast
- Castalia
- caste
- castellanus
- Castilla, Ramón (1797–1867)
- casting out nines
- cast iron
- castle
- Castlecliffian
- Castle Hill Uprising (1804)
- castle koppie
- Castlemainian
- Castlereagh, Robert Stewart, Viscount (1769–1822)
- Castner, Hamilton Young
- Castner–Kellner cell
- Castner–Kellner process
- Castor
- castor oil
- Castro, Fidel (1927–2016)
- cast shadow
- casual
- casualism
- casuistry
- CAT