The respiratory organ of air-breathing vertebrates. A pair of lungs is situated in the thorax, within the ribcage. Each consists essentially of a thin moist membrane that is folded to increase its surface area. Exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide takes place between blood capillaries on one side of the membrane and air on the other. The lung is supplied with air through a bronchus. In mammals and reptiles the membrane of the lung takes the form of numerous sacs (see alveolus) that are connected to the bronchus via bronchioles (see illustration). The lungs themselves contain no muscular tissue and are ventilated by respiratory movements, the mechanisms of which vary with the species.
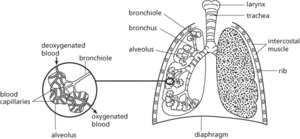
The lungs and air passages of a mammal (right lung cut open to show internal structure)
- basin modelling
- basis
- basis(of a topology)
- basis of calculation
- basis of design
- basis point
- basis vector
- basket cell
- basket centrifuge
- basket-makers
- Basleoan
- basophil
- Basov, Nikolai Gennadievich (1922–2001)
- Basov, Nikolai Gennediyevich
- Basov, Nikolai Gennediyevitch (1922–2001)
- Basque
- basset
- Bassett, Charles, II (1931–66)
- bast
- Bastiat, Frédéric (1801–50)
- bastide
- Bastille
- bastion
- bastion host
- bastnäsite