A thermometer for measuring small changes of temperature. It consists of a mercury-in-glass thermometer with a scale covering only 5 or 6°C calibrated in hundredths of a degree. It has two mercury bulbs, the range of temperature to be measured is varied by running mercury from the upper bulb into the larger lower bulb. It is used particularly for measuring depression of freezing point or elevation of boiling point of liquids when solute is added, in order to find relative molecular masses. The instrument was invented by the German chemist E. O. Beckmann (1853–1923).
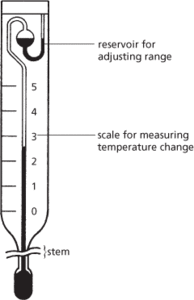
Beckmann thermometer.
A thermometer for measuring small changes of temperature (see illustration). It consists of a mercury-in-glass thermometer with a scale covering only 5 or 6°C calibrated in hundredths of a degree. It has two mercury bulbs, the range of temperature to be measured is varied by running mercury from the upper bulb into the larger lower bulb. It is used particularly for measuring depression of freezing point or elevation of boiling point of liquids when solute is added, in order to find relative molecular masses.
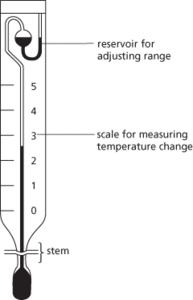
Beckmann thermometer