A test for comparing two (or more) sets of survival times (see hazard rate). The data consist of the completed lifetimes of individuals who have died and the current ages of those still living. The null hypothesis is that the sets come from the same population. Suppose there are m distinct survival times, t(1)<t(2)<⋯< t(m). For the two-sample case the test statistic is g, given by
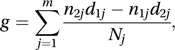 where nkj is the number of individuals in set k who are alive just before time t(j), dkj is the number of these who die at that time, and Nj=n1j+n2j.
where nkj is the number of individuals in set k who are alive just before time t(j), dkj is the number of these who die at that time, and Nj=n1j+n2j.The distribution of g can be approximated by a normal distribution with, under the null hypothesis, mean 0 and variance V, where
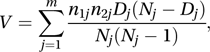 and Dj=d1j+d2j.
and Dj=d1j+d2j.
- year
- yeast
- yeast artificial chromosome
- yeasts
- yeast two-hybrid screen
- yedoma permafrost
- Yegorov, Boris B. (1937–1994)
- yellow body
- Yellow Book
- yellowcake
- yellow Ethernet
- yellow pages
- yellow page service
- Yeltsin, Boris (1931–2007)
- Yemen, Republic of
- yen
- yeoman
- Yepun
- Yerkes Observatory
- Yerkes system
- yew
- yi
- yield
- yield curve
- yield gap