An idealized representation of an electronic device that executes a logical operation such as and, or, or not. The standard symbols for those gates are drawn below. Logic gates may then be combined in circuits to produce more complicated n-ary logical operations. See combinatorial logic.
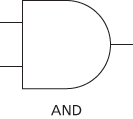
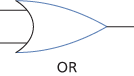
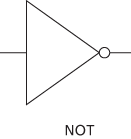
A device, usually but not exclusively electronic, that implements an elementary logic function; examples include AND, OR, NAND, and NOR gates, and inverters. There are typically between two and eight inputs and one or two outputs. In order to represent the two logic states, true and false, in electronic logic gates, the input and output signals are held at either of two different voltage levels; a high voltage level usually represents true (logic 1) and a low level false (logic 0).
Each type of logic gate has a logic symbol that conveys its logic function but does not indicate the electronic circuitry involved. The use of these symbols in circuit diagrams simplifies the understanding of a complex logic circuit and means that technological advances in electronics need not be taken into account.
Logic gates based on fluid logic have been successfully used as have optical switches used as logic gates. See also digital logic, logic circuit, multivalued logic.
A digital circuit, such as an AND gate, that implements an elementary logical function. It has one or more inputs but only one output. The conditions applied to the input(s) determine the voltage levels at the output. The output usually has two possible output states: ‘1’, ‘0’. See logic circuit; tristate logic gate.
- sideband
- sideband splatter
- sideblog
- side chain
- side effect
- side-effects
- side formula
- side frequency
- side hatch
- side lobe
- side-looking airborne radar
- side-payment
- side reaction
- sidereal
- sidereal day
- sidereal month
- sidereal period
- sidereal rate
- sidereal time
- sidereal year
- Siderian
- siderite
- siderolite
- siderophile
- siderophyre