A temperature driving force applied to the heat transfer between fluids with constant heat capacities. It is applied to fluids that transfer heat in countercurrent directions and is determined from the difference in the temperature difference in fluid temperatures at either end of the heat exchanger divided by the natural logarithm of the ratio of the same two temperature differences:
It should not be used where the overall heat transfer coefficient varies appreciably, with multipass heat exchangers, nor where heat is generated such as on one side of the heat transfer surface as in an exothermic reaction in a water-cooled reactor (see Fig. 27).
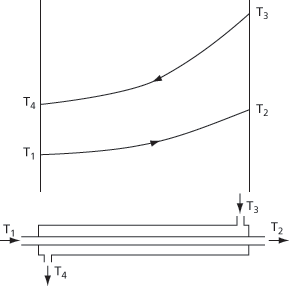
Fig. 27 Log mean temperature difference
- GLC
- glebe
- Gleedonian
- Glejser test
- Glencoe, Massacre of (13 February 1692)
- Glendower, Owen (1354–c.1417)
- Glenn, John Herschel, Jr. (1921)
- Glenn, John Jr (1921–2016)
- Glenn Research Center
- glenoid cavity
- Glen’s Flow Law
- Glen’s power flow law
- gley
- gleying
- gley soil
- gley soils
- gleysols
- gleyzation
- glia
- glide
- glide reflection
- glideslope
- gliding tectonics
- gliding twins
- GLIM