1. The periodic rise and fall of the Earth’s oceans, caused by the relative gravitational attraction of the Sun, Moon, and Earth. The effect of the Moon is about twice that of the Sun, giving rise to the spring–neap cycle of tides. Variation in tides is caused by: (a) changes in the relative positions of the Sun, Moon, and Earth; (b) uneven distribution of water on the Earth’s surface; and (c) variation in the sea-bed topography. Semi-diurnal tides are those with two high and two low waters (period 12 hours and 25 minutes) during a tidal day (24 hours and 50 minutes). Diurnal tides have one high and one low water during a tidal day.
2. See earth tides.
Tide
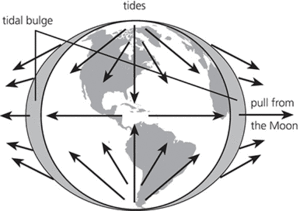
Tides result from the gravitational pull of the moon and sun on the Earth (which also affects land masses, but the reaction of the water is greater and more apparent). The greatest effect of this pull is on each side of the Earth as it faces the moon. The moon ‘pulls out’ two bulges of water, which are fixed—the Earth moves through them, causing high water twice daily. The sun also attracts water. When the effects of both sun and moon coincide, twice monthly in the second and fourth quarters of the moon, high spring tides occur. When the sun and moon seem to be at right angles to each other from the Earth, the forces of moon and sun are opposed to each other, and lower, neap tides result. The dynamic tide theory suggests that the global tidal water motion is broken up into a large number of tidal systems, constrained by the coastal topography, and known as amphidromes. The tides travel around the centre of the amphidrome as a wave.
- women’s movement
- women’s suffrage
- Wonokan
- wood
- wood alcohol
- woodcock
- woodlouse
- woodpecker
- wood tin
- Woodward, John (1665–1728)
- Woodward, Robert Burns
- Woodward, Robert Burns (1917–79)
- Woodward–Hoffmann rules
- Wood’s metal
- woofer
- Woolley, Richard van der Riet (1906–86)
- woolsack
- wool staple
- Word
- word
- word-addressable
- Worden, Alfred Merrill (1932–2020)
- Wordian
- word length
- word line