Measures of location, spread, and other properties of distributions that are computed from linear combinations of the ordered data values x(1)≤x(2)≤⋯≤x(n) (with mean x̄, which is the first L-moment). Defining the quantities b1, b2,…,bn−1 by
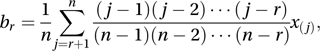 the next three L-moments are 2b1 − x̄, 6b2 − 6b1 + x̄, and 20b3−30b2+12b1−x̄. The second L-moment is related to the Gini statistic. An advantage of L-moments is that they can be calculated even when distributions have infinite variances.
the next three L-moments are 2b1 − x̄, 6b2 − 6b1 + x̄, and 20b3−30b2+12b1−x̄. The second L-moment is related to the Gini statistic. An advantage of L-moments is that they can be calculated even when distributions have infinite variances.
- modem optimizer
- mode of production
- moder
- moderated
- moderated newsgroup
- moderately repetitive DNA
- moderation
- moderator
- modern control
- modernism
- modernity
- modernization theory
- modern synthesis
- modesty
- MODFET
- modifiable areal units
- Modified Julian Date
- modified Newtonian dynamics
- Modified units
- modifier bits
- modifier gene
- Modigliani–Miller theorem
- mod-n counter
- Modula
- Modula 2