See complex number.
A synonym for complex plane.
A graphical way of representing complex numbers in the form in which real and imaginary parts of the complex number are the x and y axes, respectively (see Fig. 2). The modulus is the distance z and the angle of z is the argument. It is named after Swiss mathematician Jean-Robert Argand (1768–1822) and is useful in understanding the stability of controlled processes.
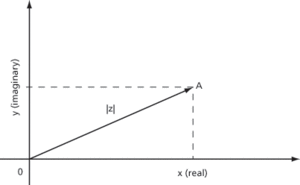
Fig. 2
See complex plane.
- PIPO
- Pippard, Sir Alfred Brian
- piracy
- piranha
- Pirani gauge
- PIR detector
- Piripauan
- piRNA
- pirsonnite
- Pisces
- Piscis Austrinid meteors
- Piscis Austrinus
- Pishgam
- doubt
- doubt, Cartesian
- doughnut city
- Douglas Aircraft Company
- Douglas, Clifford (1879–1952)
- Douglas-Home, Sir Alec (1903–95)
- Douglass, Andrew Ellicott
- Douglass, Frederick (1817–95)
- dove
- Dowding, Hugh Baron (1882–1970)
- Dow, Herbert Henry (1866–1930)
- do-while loop