in open systems interconnection (OSI). See seven-layer reference model.
Many computer systems are defined in terms of a layered architecture; for example, the OSI Reference Model. Each layer provides functionally distinct services to the other layers, with each layer drawing on services provided by the next layer.
Communications software is often divided into layers, each layer comprising a protocol with responsibility for a specific task. For example, a network layer protocol is responsible for getting packets from the transmitter to the receiver through many intermediate nodes; a data-link layer protocol is responsible for negotiating access to a shared medium (for example a local Ethernet LAN). The most frequently quoted model is the ISO OSI 7-layer protocol stack, in which the layers are: application, presentation, session, transport, network, data link, and physical.
‘The visual representation of a geographic dataset in any digital map environment. Conceptually, a layer is a slice or stratum of the geographic reality in a particular area, and is more or less equivalent to a legend item on a paper map. On a road map, for example, roads, national parks, political boundaries, and rivers might be considered different layers’ (ESRI GIS dictionary).
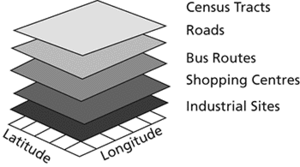
layer
- secondary emission
- secondary enrichment
- secondary failure
- secondary front
- secondary geochemical differentiation
- secondary geochemical dispersion
- secondary growth
- secondary immunological response
- secondary index
- secondary industry
- secondary-ion mass spectrometry
- secondary-ion mass spectroscopy
- secondary market
- secondary matrix
- secondary memory
- secondary metabolite
- secondary migration
- secondary mineral
- secondary minimum
- secondary mirror
- secondary oxygen pack
- secondary porosity
- secondary productivity
- secondary qualities
- secondary quartz