A cyclical series of biochemical reactions that is fundamental to the metabolism of aerobic organisms, i.e. animals, plants, and many microorganisms. The enzymes of the Krebs cycle are located in the mitochondria and are in close association with the components of the electron transport chain. The two-carbon acetyl coenzyme A (acetyl CoA) reacts with the four-carbon oxaloacetate to form the six-carbon citrate. In a series of seven reactions, this is reconverted to oxaloacetate and produces two molecules of carbon dioxide. Most importantly, the cycle generates one molecule of guanosine triphosphate (GTP – equivalent to 1 ATP) and reduces three molecules of the coenzyme NAD to NADH and one molecule of the coenzyme FAD to FADH2. NADH and FADH2 are then oxidized by the electron transport chain to generate three and two molecules of ATP respectively. This gives a net yield of 12 molecules of ATP per molecule of acetyl CoA.
Acetyl CoA can be derived from carbohydrates (via glycolysis), fats, or certain amino acids. (Other amino acids may enter the cycle at different stages.) Thus the Krebs cycle is the central ‘crossroads’ in the complex system of metabolic pathways and is involved not only in degradation and energy production but also in the synthesis of biomolecules. It is named after its principal discoverer, Sir Hans Adolf Krebs.
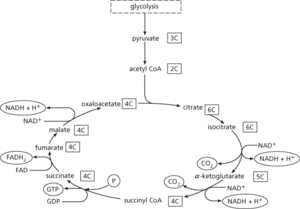
Krebs cycle
A cyclical series of biochemical reactions that is fundamental to the metabolism of aerobic organisms, i.e. animals, plants, and many microorganisms (see illustration). The enzymes of the Krebs cycle are located in the mitochondria in eukaryotes, and are in close association with the components of the electron transport chain. The two-carbon acetyl coenzyme A (acetyl CoA) reacts with the four-carbon oxaloacetate to form the six-carbon citrate. In a series of seven reactions, this is reconverted to oxaloacetate and produces two molecules of carbon dioxide. Most importantly, the cycle generates one molecule of guanosine triphosphate (GTP—equivalent to 1 ATP) and reduces three molecules of the coenzyme NAD to NADH and one molecule of the coenzyme FAD to FADH2. NADH and FADH2 are then oxidized by the electron transport chain to generate three and two molecules of ATP respectively (depending on the values of their respective P/O ratios). This gives a net yield of 12 molecules of ATP per molecule of acetyl CoA.
Acetyl CoA can be derived from carbohydrates (via glycolysis), fats, or certain amino acids. (Other amino acids may enter the cycle at different stages.) Thus the Krebs cycle is the central ‘crossroads’ in the complex system of metabolic pathways and is involved not only in degradation and energy production but also in the synthesis of biomolecules. It is named after its principal discoverer, Hans Krebs.
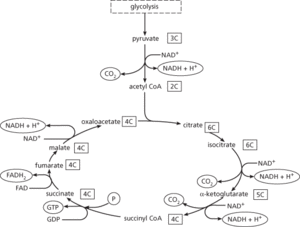
Krebs cycle
- set difference
- Setebos
- SETI
- set-on tee
- set point
- sets
- setter
- set-theoretic paradoxes
- set theory
- setting
- setting circle
- settlement
- Settlement, Act of
- settlement hierarchy
- settlement pattern
- settlement risk
- settling lag
- settling tank
- settling time
- settling zone
- set-top box
- set-up
- set-up scale instrument
- set-up time
- Sevastyanov, Vitali I (1935–2010)