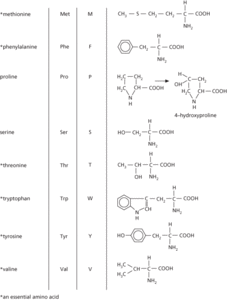
Any of a group of water-soluble organic compounds that possess both a carboxyl (–COOH) and an amino (–NH2) group attached to the same carbon atom, called the α-carbon atom. Amino acids can be represented by the general formula R-CH(NH2)COOH. R may be hydrogen or an organic group and determines the properties of any particular amino acid. Through the formation of peptide bonds, amino acids join together to form short chains (peptides) or much longer chains (polypeptides). Proteins are composed of various proportions of about 20 commonly occurring amino acids (see table). The sequence of these amino acids in the protein polypeptides determines the shape, properties, and hence biological role of the protein. Some amino acids that never occur in proteins are nevertheless important, e.g. ornithine and citrulline, which are intermediates in the urea cycle.
Plants and many microorganisms can synthesize amino acids from simple inorganic compounds, but animals rely on adequate supplies in their diet. The essential amino acids must be present in the diet whereas others can be manufactured from them.
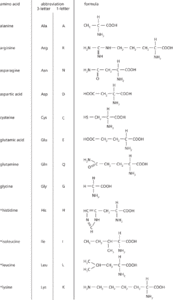
The amino acids occurring in proteins Amino acid
https://www.qmul.ac.uk/sbcs/iupac/AminoAcid/ Information about IUPAC nomenclature
Any of a group of water-soluble organic compounds that possess both a carboxyl (–COOH) and an amino (–NH2) group attached to the same carbon atom, called the α-carbon atom. Amino acids can be represented by the general formula R-CH(NH2)COOH. R may be hydrogen or an organic group, which may be nonpolar, basic, acidic, or polar; the nature of the R group determines the properties of any particular amino acid. Through the formation of peptide bonds, amino acids join together to form short chains (peptides) or much longer chains (polypeptides). Proteins are composed of various proportions of about 20 commonly occurring amino acids (see table). The sequence of these amino acids in the protein polypeptides determines the shape, properties, and hence biological role of the protein. Some amino acids that never occur in proteins are nevertheless important, e.g. ornithine and citrulline, which are intermediates in the urea cycle. (See table.)
Plants and many microorganisms can synthesize amino acids from simple inorganic compounds, but animals rely on adequate supplies in their diet. The essential amino acids must be present in the diet whereas others can be manufactured from them.

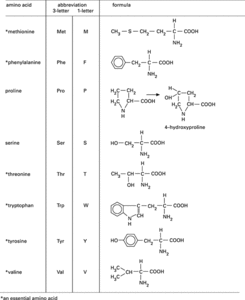
The amino acids occurring in proteins
http://biomodel.uah.es/en/model3/aa.htm Depicts molecular structures of all the amino acids
Organic compound containing an acidic carboxyl (COOH) group and a basic amino (NH2) group. They constitute the fundamental building blocks of peptides and proteins and are classified either (a) as neutral, basic, or acidic (according to their pH), or (b) as non-polar, polar, or charged (according to their electrical configuration).
- Croce, Benedetto (1866–1952)
- crocidolite
- Crockett, David (1786–1836)
- Crocodilia
- Croesus (560–546)
- Croixian
- Croll, James
- Cromerian
- Crommelin
- Crommelin, Andrew Claude de la Cherois (1865–1939)
- Cromwell current
- Cromwell, Oliver (1599–1658)
- Cromwell, Richard (1626–1712)
- Cromwell, Thomas (1485–1540)
- Cronbach, Lee Joseph (1916–2001)
- Cronbach's alpha
- Cronin, James Watson
- cronstedite
- Crookes dark space
- Crookes, Sir William
- Crookes, Sir William (1832–1919)
- crop
- cropping
- crop rotation
- Crosland, Anthony (1918–77)