Probability distributions, of widely differing shapes, that can be obtained by simple transformations of the standard normal distribution. The relationship to the normal distribution makes it easy to calculate, for example, a tail probability (see tail area). The entire family is defined by
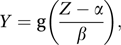 where α and β are constants, g is a function, Z is a standard normal random variable and Y is a random variable having a Johnson distribution.
where α and β are constants, g is a function, Z is a standard normal random variable and Y is a random variable having a Johnson distribution.There are three classes of Johnson distributions, referred to as the SU, SB, and SL classes, which result from different choices for the function g(x). In the order given, for a variable x, the functions are
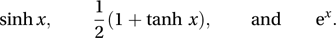 The last case gives a type of lognormal distribution.
The last case gives a type of lognormal distribution.
- clastic
- clastic dyke
- clastic rock
- clastogenic flow
- clathrate
- clathrin
- Claude, Albert
- Claude, Georges (1870–1960)
- Claude process
- claudetite
- Claudius (10 bc–54)
- clausal normal form
- clause
- Clausewitz, Karl von (1780–1831)
- Clausius inequality
- Clausius, Rudolf Julius Emmanuel
- Clausius, Rudolf Julius Emmanuel (1822–88)
- Clausius, Rudolph Julius Emmanuel (1822–88)
- Clausius–Clapeyron equation
- Clausius–Mossotti equation
- Claus process
- Clavatipollenites
- clavicle
- Clavius’ law
- clay