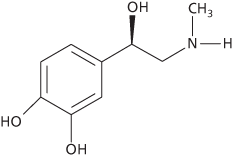
A hormone, produced by the medulla of the adrenal glands, that increases heart activity, improves the power and prolongs the action of muscles, and increases the rate and depth of breathing to prepare the body for ‘fright, flight, or fight’. At the same time it inhibits digestion and excretion.
Adrenaline
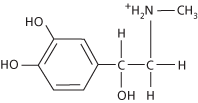
A hormone (see formula), produced by the medulla of the adrenal glands, that increases heart rate and blood pressure, improves the power and prolongs the action of muscles, and increases the rate and depth of breathing to prepare the body for ‘fright, flight, or fight’ (see alarm response). At the same time it inhibits digestion and excretion and stimulates the mobilization of body fat (lipolysis) and glycogen stored in the liver, hence increasing the concentration of glucose in the blood for energy metabolism (glycolysis). Similar effects are produced by stimulation of the sympathetic nervous system. Adrenaline causes these effects by binding to adrenoceptors on target cells. It can be administered by injection to relieve bronchial asthma and reduce blood loss during surgery by constricting blood vessels. See adrenoceptor.
Adrenaline
- pope
- P operation
- Poperinge
- Popish Plot (1678)
- POPL
- poplar
- Pople, John A.
- POPLOG
- Popov, Aleksandr Stepanovich
- Popovich, Pavel Romanovich (1930–2009)
- Popper, Karl Raimund (1902–1994)
- poppy
- pop-shooting
- Popular Front
- population
- population bottleneck
- population census
- population correlation coefficient
- population covariance
- population density
- population dynamics
- population ecology
- population equation
- population genetics
- population geography